What is a dental implant? Basic definition and general information
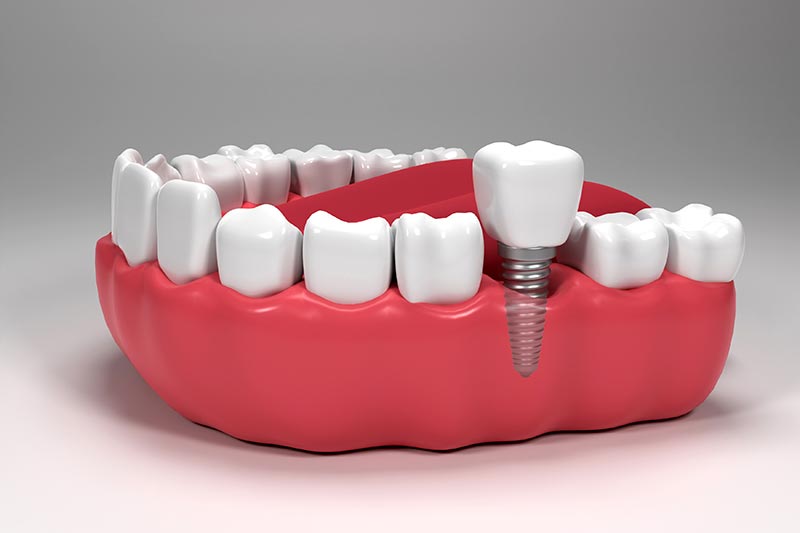
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots, usually made of titanium, that are inserted into the jawbone to replace missing teeth. The goal of this method is to mimic the function and appearance of natural teeth as closely as possible. Implants are widely used in modern dentistry and offer a long-term and reliable solution for aesthetic and functional gaps in the teeth.
The main purpose of dental implants is to provide permanent and stable support for missing teeth while protecting the surrounding healthy teeth. Implants can fuse with the jawbone. This process, called osseointegration, occurs through the ingrowth of the titanium material into the bone tissue.
Advantages of dental implants
- Natural look: Implants mimic the natural tooth structure by taking over the function of the natural tooth root.
- Durability: They are durable because they are made from high-quality materials.
- Jawbone health: Prevents weakening or loss of the jawbone.
- Comfort: It is significantly more comfortable than removable dentures.
- Speech and chewing function: It replaces lost teeth and enables full chewing and clear speech again.
The patient’s assessment is crucial for determining implant suitability. Dentists create an individualized treatment plan, taking into account the patient’s overall health, jawbone density, and gum health. Chronic conditions such as smoking, poor oral hygiene, and diabetes can negatively impact the success of implants. Therefore, the dental examination is the starting point for a process tailored to each individual patient.
Dental implants are considered a treatment option that improves quality of life by combining aesthetics and functionality. The more carefully the individual treatment phases are planned, the more successful the result.
Types and applications of dental implants
Dental implants are among the most advanced treatment methods in dentistry for replacing missing teeth and preserving jaw structure. There are various types of dental implants, each designed for different needs. A detailed examination of each type and its respective applications will help in making the right decision for individual treatment.
Types of dental implants
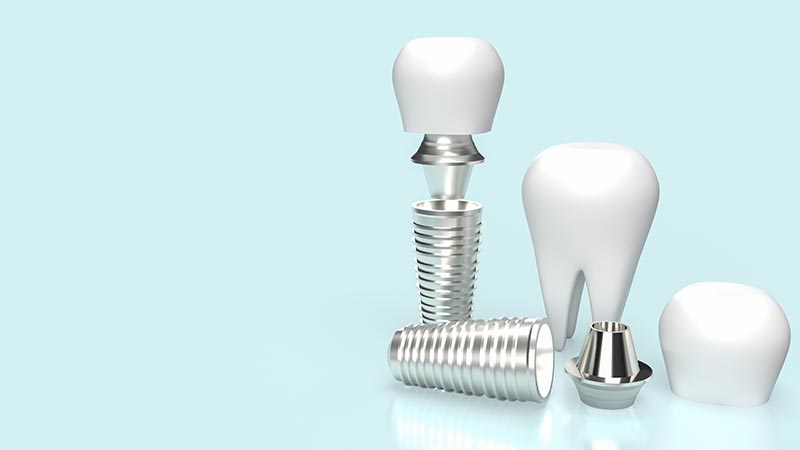
- Endosteal (intraosseous) implants This type of implant is the most commonly used. It is inserted into the jawbone and usually has a screw- or cylinder-shaped form. It is made of biocompatible materials such as titanium or zirconium. It is particularly suitable for patients with extensive tooth loss and good bone density.
- Subperiosteal (lying above the bone) implants This type of implant, which is placed on the bone below the gum line, offers a solution for people with insufficient jawbone density. It typically consists of a metal framework and is supported by a prosthesis.
- Cheekbone implants These implants, used in patients with severe bone loss in the posterior region of the upper jaw, are placed in the cheekbone. They require a different technique and a more complex insertion process than other implants.
Application areas
- In the case of a single missing tooth: It serves to replace the root of a single tooth in cases of tooth loss. In this case, a natural appearance can be achieved without damaging the surrounding teeth.
- In cases of multiple missing teeth: It serves as a support for bridge prostheses in cases where more than one tooth is missing.
- Complete tooth loss: Dental implants can be used in combination with a full denture to replace all teeth.
- Supportive jaw functions: It is an effective treatment method for protecting the jaw structure and preventing osteoporosis.
Every patient can find the right type of implant and treatment method for them. The selection depends on factors such as jaw structure, gum condition, and the number of missing teeth. Based on these criteria, the dentist determines the most suitable method.
Who are dental implants suitable for?
Dental implants are an effective method for replacing missing teeth, both functionally and aesthetically. However, this treatment is not suitable for everyone. Factors that determine suitability for dental implants include general health, jawbone quality, and age.
Generally, dental implant treatment is suitable for people in good overall health. However, a medical examination is essential for those with diabetes, heart disease, or other chronic illnesses. Since overall health can directly influence the healing process, a thorough medical examination should be conducted.
The condition of the jawbone is also a crucial factor in the suitability of implants. In individuals with insufficient healthy bone tissue, adequate implant retention may not be guaranteed. In such cases, preparatory measures such as bone grafting may be necessary. Therefore, the volume and density of the jawbone must be assessed.
Furthermore, dental implant treatment is generally only suitable for individuals whose bone growth is complete. Therefore, the treatment is not recommended for people under 18 years of age. This treatment method is considered more suitable for adults than for children.
Meticulous oral hygiene is crucial for the success of the treatment. If oral hygiene is neglected, infections can occur around the implant, negatively impacting the outcome. Furthermore, delayed wound healing in smokers can complicate the treatment process and increase the risks.
Therefore, anyone considering dental implant treatment should undergo a thorough examination by a dentist. The oral structure and overall health of each individual must be assessed for this treatment.